How does minoxidil work for hairfall : A comprehensive guide to understand your unique hairfall needs
Minoxidil is a widely used and FDA-approved medication for treating hair loss in both men and women. Originally developed as an oral medication to treat high blood pressure, it was later discovered that one of its side effects—hair regrowth—could be harnessed to combat hair thinning and baldness. Today, minoxidil is commonly applied topically in liquid or foam form and is available over-the-counter under brand names like Rogaine, as well as in generic versions. Understanding how minoxidil works involves examining its effects on the hair growth cycle and the scalp.
Mechanism of Action:
Minoxidil’s exact mechanism in promoting hair growth is not fully understood, but several key effects are believed to contribute to its effectiveness:
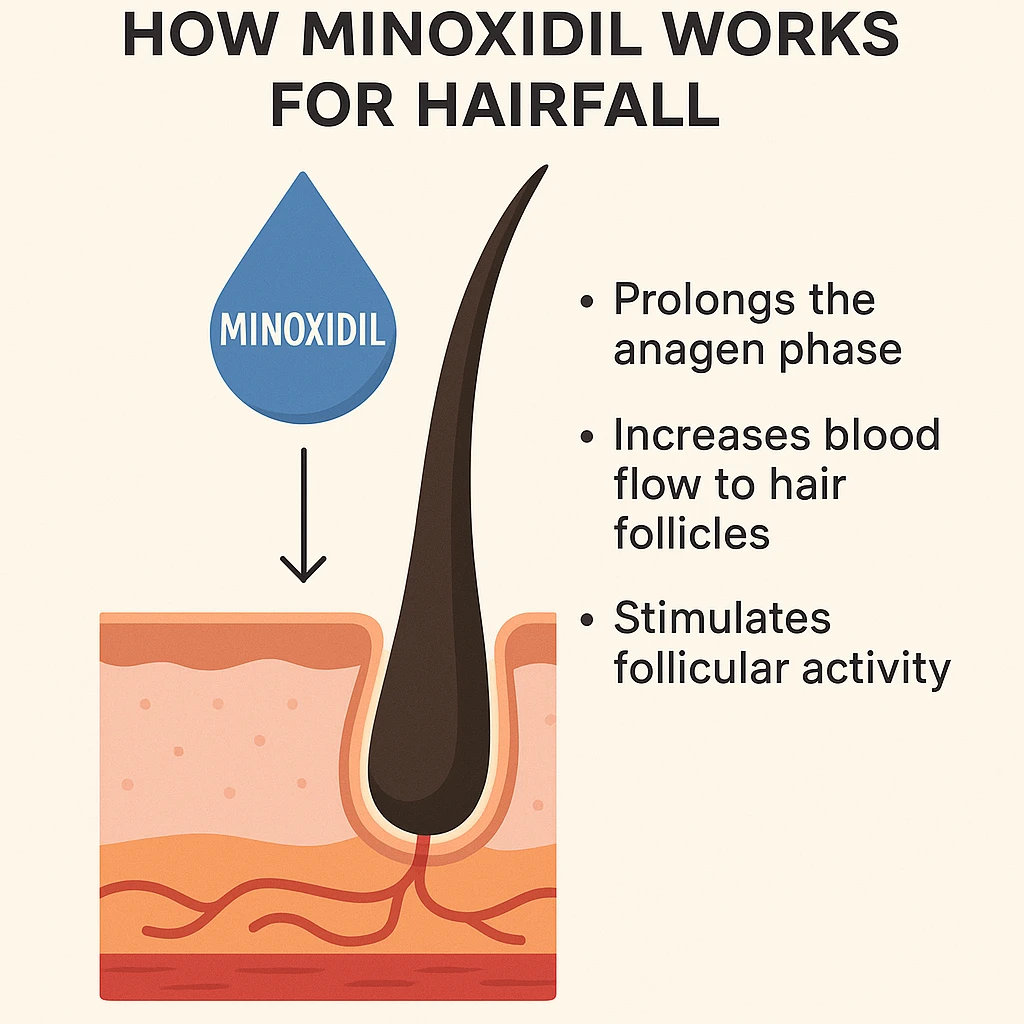
1. Prolongs the Anagen Phase:
Hair grows in cycles, including the growth (anagen), resting (telogen), and shedding (catagen) phases. In people experiencing hair loss, the anagen phase becomes shorter, leading to thinner, weaker hairs and more time spent in the resting phase. Minoxidil helps prolong the anagen phase, encouraging more hair to stay in the growth cycle for longer periods. This leads to increased hair density and thicker strands over time.
2. Increases Blood Flow to Hair Follicles:
Minoxidil is a vasodilator, meaning it widens blood vessels. When applied to the scalp, it is believed to improve blood circulation in the area, increasing the delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and growth factors to hair follicles. This enhanced microcirculation may help revive miniaturized (shrinking) follicles and support their return to a healthy, productive state.
3. Stimulates Follicular Activity:
Minoxidil is thought to stimulate follicular epithelial cells directly, encouraging dormant or less active hair follicles to enter the anagen phase and start producing hair again. This can result in new hair growth, particularly in individuals with early-stage hair loss.
4. Increases Hair Follicle Size:
Hair follicles affected by androgenetic alopecia tend to shrink over time, producing finer and weaker hairs. Minoxidil may reverse this process by enlarging the follicles, leading to the growth of thicker and more pigmented hair strands.
Effectiveness:
Minoxidil is most effective in people with recent or early hair loss, particularly in the crown and vertex areas of the scalp. It is less effective for receding hairlines or extensive baldness. Consistent application is crucial—most users see visible results after 3 to 6 months of daily use, and continued application is necessary to maintain those results. Once discontinued, any new hair growth typically falls out within a few months.
Side Effects:
Minoxidil is generally safe but may cause some side effects, including scalp irritation, dryness, flaking, and unwanted facial hair growth due to accidental contact. In rare cases, systemic absorption may lead to symptoms like rapid heartbeat or dizziness.
Conclusion:
Minoxidil works by prolonging the growth phase of hair, enhancing blood flow to hair follicles, and reviving dormant follicles. Although it is not a cure for hair loss, especially genetic types like androgenetic alopecia, it can significantly slow down the process and even regrow hair in some individuals. Consistency, patience, and proper application are key to achieving optimal results.
Related Blog
What Causes Oily Skin and Can It Be Managed Naturally? Exploring Root Causes and Gentle Solutions
Aug 2, 2025 by Admin
General
What Are the Signs That You Have Sensitive Skin? Key Symptoms to Help You Identify This Delicate Skin Type
Aug 1, 2025 by Admin
General