How Can You Tell if a Fungal Infection Is Causing the Itch? Recognizing Signs and Symptoms for Timely Care
How Can You Tell if a Fungal Infection Is Causing the Itch? Recognizing Signs and Symptoms for Timely Care
Itchy skin can be triggered by many different conditions—dryness, allergies, irritation, or even underlying health issues. But one of the most common causes, especially on the feet, groin, and other warm, moist areas, is a fungal infection. Knowing how to recognize the telltale signs of a fungal itch can help you act quickly, relieve discomfort, and prevent the infection from spreading or worsening. Here’s what to look for.
Why Fungal Infections Cause Itch
Fungal infections, like those caused by dermatophytes (Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, etc.), feed on keratin—a protein found in your skin, hair, and nails. As the fungus grows, it irritates the skin, leading to inflammation and itching. The itch is often persistent and may worsen after sweating or wearing tight clothing.
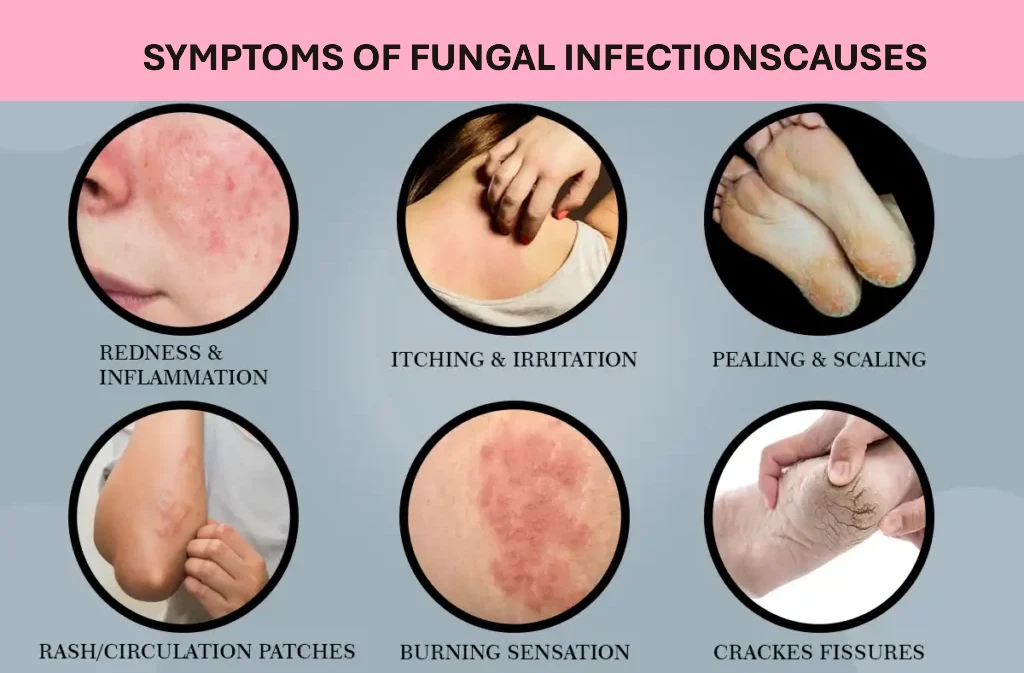
Key Signs That Point to a Fungal Infection
-
Red, Scaly Patches
Fungal infections often create well-defined patches of red or pink skin. The texture can appear scaly, flaky, or slightly raised around the edges. This is common in conditions like athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) or ringworm (tinea corporis). -
Itch That Doesn’t Go Away
The itch from fungal infections tends to be stubborn and constant, unlike the brief itch from dry skin. It may even feel more intense at night or after exercise. -
Circular or Ring-Shaped Rash
In ringworm, the infection often forms a circular or ring-like rash with a clear center and a raised, scaly border. This classic pattern makes it easier to recognize. -
Peeling, Cracking, or Fissures
In athlete’s foot, the skin—especially between the toes—may peel, crack, or develop small painful splits. These fissures can itch and sometimes burn. -
Thickened or Discolored Nails
If the fungus spreads to the nails, they may become thick, brittle, and yellowish or brown. This can accompany itching around the nail bed. -
Moist, Macerated Skin
Areas that stay damp, like between toes or in skin folds, may look soft, white, and wrinkled, with an associated musty odor. This environment encourages fungal growth.
Areas Most Commonly Affected
-
Feet (Athlete’s foot): Itchy, peeling, often between the toes or on the sole.
-
Groin (Jock itch): Itchy, red patches with defined edges on the inner thighs or groin area.
-
Body (Ringworm): Circular, itchy patches anywhere on the body.
-
Scalp or nails: Flaking, thickening, or discoloration.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If your itch persists for more than a few days, spreads quickly, or is accompanied by cracking, oozing, or pain, it’s wise to see a dermatologist. They can confirm the diagnosis with a simple skin scraping or culture and recommend effective antifungal treatments.
Treatment and Prevention Tips
-
Use over-the-counter antifungal creams, sprays, or powders as directed.
-
Keep affected areas clean and dry.
-
Change socks and underwear daily.
-
Avoid walking barefoot in communal areas like gyms or pools.
-
Wash towels and clothes in hot water to kill fungal spores.
Conclusion
While itching alone doesn’t always mean you have a fungal infection, a persistent, scaly, or ring-shaped rash is often a strong clue. Recognizing these signs early allows you to treat the infection promptly and avoid complications. Remember: healthy skin starts with paying attention to what your body is telling you.
Related Blog
What Causes Oily Skin and Can It Be Managed Naturally? Exploring Root Causes and Gentle Solutions
Aug 2, 2025 by Admin
General
What Are the Signs That You Have Sensitive Skin? Key Symptoms to Help You Identify This Delicate Skin Type
Aug 1, 2025 by Admin
General